Updates
The background of Naturopathy

Naturopathy, also known as naturopathic medicine, is a whole-system, multi-modality approach in the medicinal practice. The ‘whole-system’ refers to addressing different dimensions of an individual including the mental, spiritual, physical, family, community and environment. On the other hand, ‘multimodality’ refers to employing at least 2 or more methods in a single approach in treating an individual. Naturopathy is a holistic system that focuses on whole-patient wellness by understanding the body, mind, and spirit of the person, addressing the underlying cause of the conditions rather than treating the symptoms only. Naturopathic doctors will employ non-toxic natural therapies to restore physiological, psychological, and structural balance. Most of the naturopathic doctors use a variety of therapies and techniques such as nutrition, herbal medicine, homeopathy, manipulative therapy, exercise therapy, psychotherapy and others to promote the body’s self-healing mechanism. The two areas of focus in naturopathy are:
- supporting the body’s own healing abilities, empowering people to make lifestyle changes necessary for the best possible health.
- emphasis on health promotion and disease prevention.
The history of Naturopathy

The central tenet of naturopathy is ‘the healing power of nature’ (vis medicatrix naturae), a concept formulated by Hippocrates, who is a Greek physician to be traced back to 370 BC in ancient Greek. This concept refers to the healing ability of the living system that helps in establishing, maintaining and restoring the health of an individual. Since then, it has been the central principle of naturopathic medicine. In the last century in 1885, the word ‘naturopathy’ was first coined by a German homeopath Dr John Scheel. Then, in the year 1901, the word had been purchased by another physician Dr Benedict Lust, who is considered the father of American naturopathy, which he used the word to describe the broad practice of a naturopathic doctor. In the subsequent year, 1902, he founded the first school of naturopathic medicine in North America, which is also a place where modern naturopathic medicine had developed.
The 6 principles in Naturopathy
- Do no harm (Primum Non Nocere)
First, naturopathic doctors will use the methods and medicinal substances in minimizing the harmful side effects. Second, they would avoid any harmful suppression of symptoms whenever possible. Third, they acknowledge the person’s healing process and least force is being used in diagnosing and treating the illness.
- The healing power of nature (Vis Medicatrix Naturae)
Naturopathic doctors recognize the body’s inherent ability to heal and regenerate. They want to enhance the healing ability of the patient by identifying and removing the obstacles in the recovery process of the patient.
- Identify and treat the causes (Tolle Causam)
The interest of naturopathic doctors is to identify and remove the underlying causes of the illness more than treating the symptoms. They argue that if the symptoms of disease or illness are temporarily eliminated or suppressed without addressing the underlying causes, the problems will still return, or could even become worse.
- The physician (doctor) as teacher (Docere)
The naturopathic doctors will educate the patients on preventive healthcare and healthy living. They teach the patients the cause of illness to avoid recurrence, they also engage the patient in their own recovery journey and encourage self-responsibility of patients on their own health. This will enable the patient to make informed decisions where they are aware of the consequences of every action they take.
- Treat the whole person
Naturopathic doctors will treat the patient individually by taking into account their mental, emotional and physical state as well as genetic, environmental and social factors. They believe that when these factors are holistically integrated, only then can a person experience optimal health.
- Prevention
Naturopathic doctors emphasize disease prevention by assessing risk factors applying appropriate interventions to prevent illness.
The 7 levels of therapeutic orders
The therapeutic orders guide the practice of naturopathic medicine in treating patients. It starts from the least to the most invasive interventions, from more general to more specific therapies and strategies. This includes 7 steps of orders to be applied from the bottom-up, however, it is not rigid and the application is adapted to each individual patient.
- Establish the foundation for optimal health
Identify and remove the obstacles that may impede healing such as poor diet, excessive stress, inadequate rest. The purpose is to optimize the person’s self-healing and for future therapeutic intervention to be effective.
- Stimulate self-healing
Believe in the body’s innate healing ability and utilizing various therapies to stimulate and enhance the body’s healing.
- Support and restore weakened system
To enhance the function of the body through repairing or supporting the over or underactive system of the body.
- Address physical alignment
Using physical therapies such as spinal manipulation and massage therapy improves, supports, and maintains musculature, skeletal, and facial integrity to promote optimal structure conditions.
- Natural symptom relief
Using natural substances to relieve the symptoms which cause suffering while still focusing on restoring health.
- Synthetic symptom relief
Using synthetic or pharmaceutical substances to suppress symptoms and address the pathology that is negatively impacting the patient’s quality of life.
- High force interventions
Utilize more invasive therapies when necessary to first address the symptoms before addressing the underlying causes. It is being done until the patient is stabilized and is suitable to address the underlying causes.
References
Casarella, J., 2020. Psychotherapy [online]. WebMD. Available from: https://www.webmd.com/mental-health/mental-health-psychotherapy [Accessed 14 Aug 2021].
NCCIH, 2017. Naturopathy | NCCIH [online]. Available from: https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/naturopathy [Accessed 14 Aug 2021].
NCCIH, 2021. Homeopathy | NCCIH [online]. NCCIH. Available from: https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/homeopathy [Accessed 14 Aug 2021].
NHS, 2021. Homeopathy – NHS [online]. Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/homeopathy/ [Accessed 14 Aug 2021].
NIMH, 2021. Psychotherapies [online]. Available from: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/psychotherapies [Accessed 14 Aug 2021].
SP, M. and V, V., 2019. The State of the Evidence for Whole-System, Multi-Modality Naturopathic Medicine: A Systematic Scoping Review. Journal of alternative and complementary medicine (New York, N.Y.), 25 (2), 141–168.
LATEST

完结篇-回顾综合诊疗服务

肠道水疗
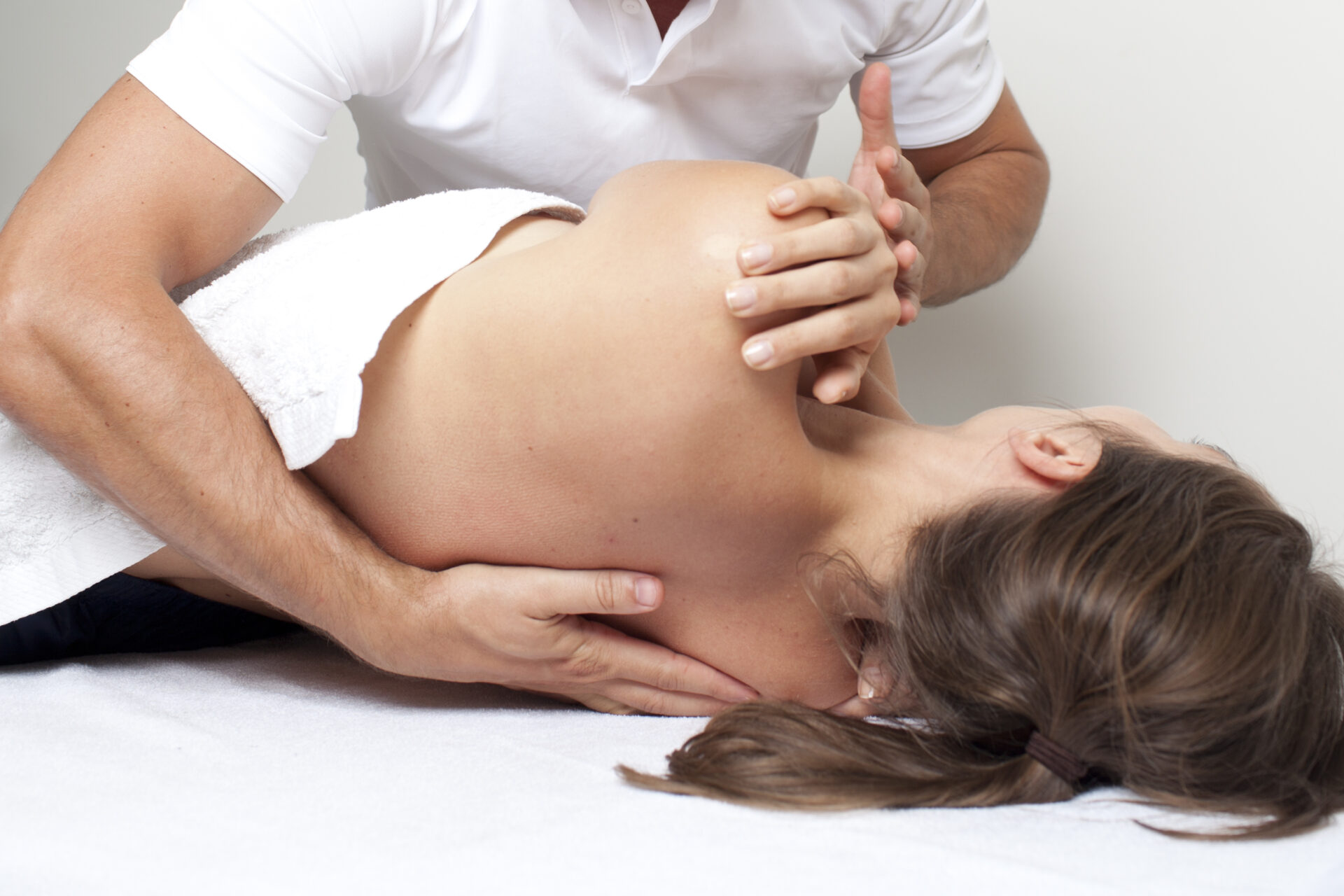
整脊疗法

芳香疗法
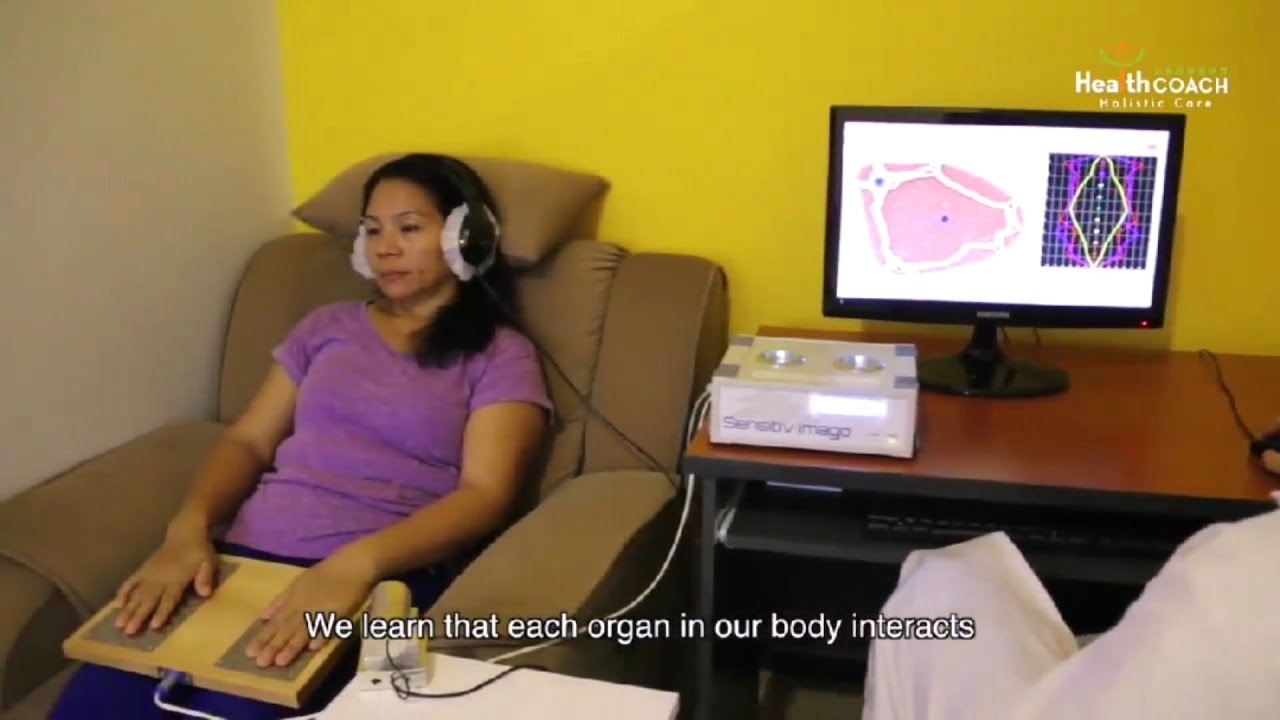
生物共振疗法
POPULAR

完结篇-回顾综合诊疗服务

肠道水疗

整脊疗法

芳香疗法
