Updates
Effect of Stevia On Blood Glucose Profile

What is Stevia?
Stevia, also known as sweet leaf, honey leaf, candy leaf, sweet weed or sweet herbs. This is due to the chemical characterization of the natural constituents of the plant known as steviol glycosides, which are responsible for its distinct sweet taste.
Stevia is gaining significant popularity in different parts of the world and is expected to be a major source of high potency sweetener. This is because stevia is a sugar substitute made from the leaves of the stevia plant. It’s about 200 to 300 times sweeter than table sugar and it has very low or no carbohydrates, calories or artificial ingredients. With zero calories, this plant is being recognized as a great replacement for sugar and other sweeteners. Thus, it is ideal for people who are conscious of sugar and carbohydrate intake.
Why is Stevia diabetic friendly?
Toxicological, biological and clinical studies showed that high-purity stevia leaf extract sweetener, called steviol glycosides, is generally recognized as safe for all individuals, including children, pregnant women and individuals with diabetes. It has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) for the antioxidant and antidiabetic properties.
Governing bodies such as Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), World Health Organization (WHO) and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have also established an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) of 4 mg/kg of body weight per day. This equates to approximately 12 mg of high-purity stevia extracts/kg of body weight per day. However, whole-leaf stevia and raw stevia extract for use in processed foods and beverages are not approved by USFDA due to a lack of safety information.
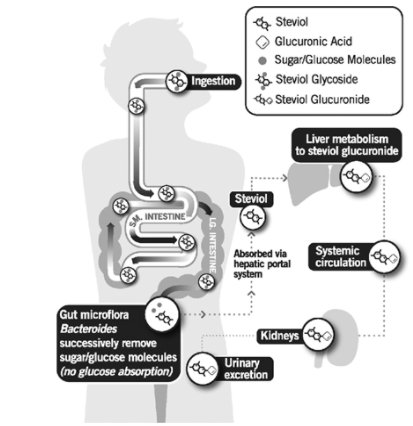
Human saliva which contains amylase enzyme is not able to hydrolyze the glycosidic bonds present in stevioside. However, the gut microbiota of human is able to degrade stevioside to steviol. This is because Bacteroides species are primarily responsible for the hydrolysis of steviol glycosides in the gut. The released sugar moieties are not absorbed and are most likely quickly utilized by the gut microbes as an energy source, thus making it a zero-calorie sweetener. After that, steviol is transported to the liver where it is conjugated with glucuronic acid to form steviol glucuronide which is then excreted in urine. Thus, it doesn’t cause blood sugar spikes.
Possible Health Benefit of Stevia
Research has shown that stevia sweeteners do not contribute calories or carbohydrates to the diet. They have also demonstrated no effect on blood glucose or insulin response. This is because one of the most important biological effects of stevia is opening calcium channels in pancreatic beta cells mediated by the active constituent of S. rebaudiana, steviol. This stimulates insulin secretion in response to glucose. On the other hand, it is also reported the benefits of stevia for healthy individuals as a preventive mechanism against insulin resistance that leads to diabetes. Therefore, use of stevia for the management of type 2 diabetes is recommended.
Side Effect of Stevia
High purified stevia leaf extract is generally recognized as safe but some stevia products contain sugar alcohol. People with sensitivity to sugar alcohol may experience bloating, abdominal cramps, nausea and diarrhea. However, as long as stevia is highly-purified and used in moderation, it will not cause side effects and can be consumed worry-free.
LATEST

完结篇-回顾综合诊疗服务

肠道水疗
整脊疗法

芳香疗法
生物共振疗法
POPULAR

完结篇-回顾综合诊疗服务

肠道水疗

整脊疗法

芳香疗法
